Cho phương trình $\Large 3^x(3^{2x}+1)-(3^x+m+2)\sqrt{3^x+m+3}=2\sqrt{

MỤC LỤC
Câu hỏi:
Cho phương trình $\Large 3^x(3^{2x}+1)-(3^x+m+2)\sqrt{3^x+m+3}=2\sqrt{3^x+m+3}$, với $\Large m$ là tham số. Có bao nhiêu giá trị nguyên âm của $\Large m$ để phương trình có nghiệm thực?
Đáp án án đúng là: A
Lời giải chi tiết:
$\Large 3^x(3^{2x}+1)-(3^x+m+2)\sqrt{3^x+m+3}=2\sqrt{3^x+m+3}$
$\Large \Leftrightarrow 3^x(3^{2x}+1)=(3^x+m+2)\sqrt{3^x+m+3}+2\sqrt{3^x+m+3}$
$\Large \Leftrightarrow 3^{3x}+3^x=(3^x+m+3)\sqrt{3^x+m+3}+\sqrt{3^x+m+3}$
$\Large \Leftrightarrow 3^{3x}+3^x=\left(\sqrt{3^x+m+3}\right)^3+\sqrt{3^x+m+3}$ (1)
Xét hàm đặc trưng $\Large f(t)=t^3+t$ có $\Large {f}'(t)=3t^2+1 > 0, \forall t\in\mathbb{R}$.
Vậy
(1) $\Large \Leftrightarrow 3^{3x}+3^x=\left(\sqrt{3^x+m+3}\right)^3+\sqrt{3^x+m+3}$
$\Large \Leftrightarrow f(3^x)=f\left(\sqrt{3^x+m+3}\right)$
$\Large \Leftrightarrow 3^x=\sqrt{3^x+m+3}$
$\Large \Leftrightarrow 3^{2x}-3^x-3=m$.
Đặt $\Large u=3^x$ với điều kiện $\Large u > 0$ và đặt $\Large g(u)=u^2-u-3$. Phương trình (*) $\Large \Leftrightarrow g(u)=m$.
Mà $\Large {g}'(u)=2u-1$, $\Large {g}'(u)=0$ $\Large \Leftrightarrow u=\dfrac{1}{2}$ ta có bảng biến thiên của $\Large g(u)$
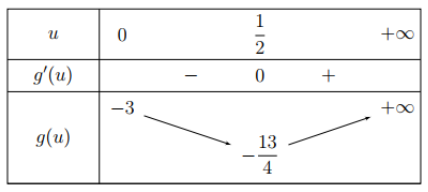
Từ bảng biến thiên ta thấy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm thực khi và chỉ khi $\Large m > -\dfrac{13}{4}$.
Vậy có tất cả 3 giá trị nguyên âm của $\Large m$ để phương trình có nghiệm thực là $\Large -3; -2; -1$.
Chọn đáp án A
Xem thêm các bài tiếp theo bên dưới
- Cho hàm số $\Large f(x)$ có đạo hàm liên tục trên $\Large \mathbb{R}.$
- Cho hình chóp S.ABC có SA vuông góc với đáy, đáy là tam giác đều, $\La
- Cho hai số phức $\Large z_1, z_2$ thỏa mãn $\Large |z_1-1+i|=1$, $\Lar
- Cho hàm số bậc ba $\Large y=f(x)=ax^3-\dfrac{1}{2}x^2+cx+d$ và parabol
- Trong không gian với hệ tọa độ $\Large Oxyz$, cho hai mặt cầu $\Large