Khi sục từ từ khí CO2 vào dung dịch Ca(OH)2. Đ
Lưu về Facebook:
MỤC LỤC
Câu hỏi:
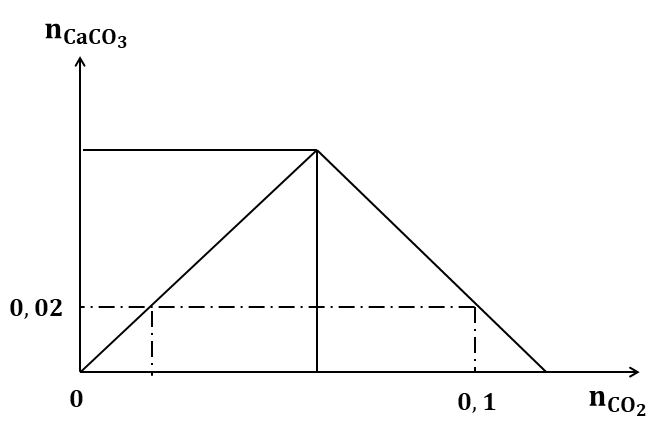
Khi sục từ từ khí CO2 vào dung dịch Ca(OH)2.

Đồ thị biểu diễn sự phụ thuộc số mol kết tủa theo số mol của CO2 như trên. Khối lượng kết tủa cực đại là:
Đáp án án đúng là: A
Lời giải chi tiết:
Khi nCO2 = 0,1 mol, kết tủa bị hòa tan một phần
nCO2=2nCa(OH)2−nCaCO3=0,1
→nCa(OH)2=0,1+0,022=0,06 mol
m↓max=100.0,06=6 g
Xem thêm các bài tiếp theo bên dưới
- Cho hỗn hợp E gồm tripeptit X có dạng Gly−M−M (được tạo nên t
- Peptit X CxHyOzN6 mạch hở tạo bởi một α-amino axit no chứ
- Hỗn hợp T gồm 3 este mạch hở X, Y, Z. Trong đó $\large M_{X} < M_{Y} <
- Trong diêm, photpho đỏ có ở đâu? Thuốc gắn ở đầu que diêm Thuốc quẹt ở
- Chọn phát biểu đúng: Photpho trắng tan trong nước không độc Photpho tr