Cho hai dao động điều hòa cùng phương với các phương trình dao động lầ
Lưu về Facebook:

MỤC LỤC
Câu hỏi:
Cho hai dao động điều hòa cùng phương với các phương trình dao động lần lượt là x1=A1cos( ω t+ π 2)(cm) và x2=A2cos( ω t+ π 6)(cm). Dao động tổng hợp của hai dao động này có phương trình là x= 30cos(ωt+φ) (cm).. Giá trị cực đại của (A1+ A2) gần nhất với giá trị nào sau đây
Đáp án án đúng là: D
Lời giải chi tiết:
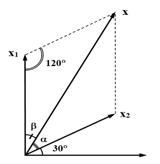
Từ hình vẽ ta có: Asin120∘=A1sinα=A2sinβ=A1+A2sinα+sinβ=A1+A22sinα+β2cosα−β2.
Suy ra A1+A2=2Asin180−1202sinα−β2sin120∘2Asin30∘sin120∘≈35cm.
Xem thêm các bài tiếp theo bên dưới
- Treo một vật vào đầu dưới của lò xo có đầu trên được giữ cố định. Khi
- Con lắc lò xo được treo thẳng đứng tại vị trí cân bằng lò xo dãn $\Lar
- Một con lắc lò xo gồm vật nặng có khối lượng 300g gắn vào lò xo. Đồ th
- Vận tốc của chất điểm dao động điều hòa có độ lớn cực đại khi nào? A.
- Một vật dao động điều hòa với phương trình: $\Large x=5\cos (\pi t-\df